Journal Articles
ABSTRACT
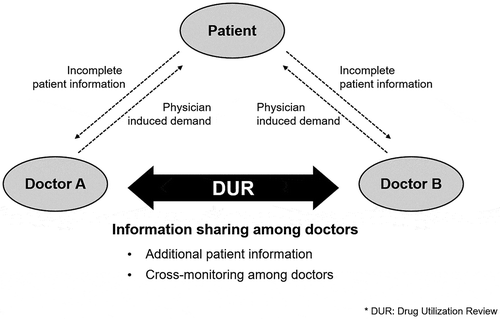
This study investigates how an increase in patient information sharing among doctors impacts healthcare costs. To this end, we explore this impact through two mechanisms – the informative role of patient health conditions and the cross-monitoring role against doctor-driven induced healthcare demands. We utilize a unique policy intervention (a drug utilization review) introduced in 2009 in Korea that enables doctors to share outpatients’ prescription histories. Using difference-in-differences, we found that, when patient information is improved, there is a reduction in pharmaceutical spending. This result is especially true for those patients who have relatively weak information-sharing capabilities. Using data on the amount of antibiotics prescribed for the common cold, we find that a cross-monitoring of prescriptions among doctors reduces the amount of unnecessary prescriptions and thus healthcare spending.